
By Ngozi Bolin, Founder, Shinkafa Inc.
Vitamin D deficiency is one of the most common nutrient deficiencies in humans.
Vitamin D has been shown to have significant impact on cancer, cardiovascular disease, bone and skin health. There is something to be said for the wonderful and caring teachers that insist that children have at least 15 minutes of daily physical education in the sun. In this publication, we will delve into the awesome benefits of vitamin D to deal with the scourge of cancer and its incredible impact in matters concerning our heart health, bone and skin health.
What exactly is vitamin D?
Vitamin D is our body’s work horse. It really is not a vitamin, per se. It functions more as a hormone and its deficiency is sadly incredibly common. Vitamin D is vital to strong bones, muscle, heart, lungs and brain functions. It helps the body fight infections and is essential to our general overall health. Once it enters the body, it becomes prepared in a way that allows it to go work to help our cells function well, reduce inflammation, help our immune system and manage calcium levels in our blood, bones and gut, for example. Deficiency in vitamin D seems to accompany just about every major disease or illness like most cases of cancer, cardiovascular disease and bone disease diagnoses.

Vitamin D is Crucial To Our Immune Functions And Overall Health
One of vitamin D’s most crucial function is its immune benefit. It keeps our immune system strong and resilient to infections, viruses and bacteria that cause illnesses. It does so by directly interacting with cells that are responsible for fighting infections. A January 2017 publication by the National Institute of Health showed a correlation between vitamin D levels and the incidence and severity of lower respiratory tracts infection, like colds and bronchitis in children. Its deficiency has been linked to lower back pain and more particularly, back pain in postmenopausal women. Further research published in October of 2010 showed a positive association of vitamin D deficiency with a variety of nonspecific bone pain, particularly in women.Vitamin D has been linked to a lower cancer risk. Vitamin D helps the body’s absorption of calcium, making both crucial to bone health.
Cedric Garland, DrPH, adjunct professor in the UC San Diego School of Medicine Department of Family Medicine and Public Health and member of Moores Cancer Center at UC San Diego Health, was quoted as saying in a report published April 6, 2016:
“We have quantitated the ability of adequate amounts of vitamin D to prevent all types of invasive cancer combined, which had been terra incognita until publication of this paper…Garland and his late brother, Frank, made the first connection between vitamin D deficiency and some cancers in 1980 when they noted populations at higher latitudes (with less available sunlight) were more likely to be deficient in vitamin D, which is produced by the body through exposure to sunshine, and experience higher rates of colon cancer. Subsequent studies by the Garlands and others found vitamin D links to other cancers, such as breast, lung and bladder.”
The world owes a great debt of gratitude for the work of the Cedric Garland and his late brother Frank Garland who pioneered this line of research and thinking. Their work, no doubt, have saved countless lives. It is thus, important to pause, give thanks and acknowledge their incredible body of work in vitamin D.
According to an April 2010 publication by the National Institute of Health captioned “Vitamin D Deficiency and Risk for Cardiovascular Disease”:
“Vitamin D insufficiency is very common in the United States and worldwide. Several recent epidemiologic studies have demonstrated a strong association between vitamin D insufficiency and risk of CVD, risk of diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Several prospective studies have suggested that vitamin D deficiency predisposes individuals to increased risk of incident hypertension, IHD, sudden cardiac death, or heart failure.”
Other studies have shown that vitamin D has benefits for dermal wound healing. Another showed that vitamin D deficiency can be a risk factor for alopecia areata where the hair loss results in hair falling out in patches. It is crucial that when one is dealing with skin and hair that care must be taken to incorporate a healthy regimen of skin care and hair care with products that are properly sourced with effective ingredients without harmful chemicals. At least one study has suggested a relationship between dosage of vitamin D and the amelioration of symptoms of depression in overweight and obese subject. Finally, Vitamin D could help extend the lives of cancer patients if taken for at least three years.

How do we get vitamin D?
Our body makes its own vitamin D from sunlight, specifically, ultraviolet B rays. This is the easiest and the most natural way to get the vitamin D that our bodies need. It could be about 15 minutes in the sun for a fair-skinned person and a while longer for a darker skinned person. Those using skin bleaching are encouraged to properly educate themselves on the harms of skin lightening and bleaching to understand the very peculiar risks they have with the exposure to certain toxic bleaching agents and thus sun exposure to this particular group comes with some risk factors. We can also get vitamin D from supplements and very small amounts come from few foods like certain fatty fish, mushrooms and vitamin D fortified foods. You should know that it is the consensus that we cannot get the required amount of vitamin D that our bodies need solely from food. Thus, exposing our skin to direct sunlight and vitamin D supplements are the effective ways to get Vitamin D that we need.
Yes, “direct sunlight.” It is was not a typo and you then ask, rather demurely, WTF gives!
We are all very familiar with the warnings by dermatologists and our surgeons general that direct sunlight is to be avoided at all costs. For decades, the sun has been demonized. So the burning question is: With the benefits of vitamin D and Ultraviolet B, how does one square the warnings of our surgeons general about avoiding sun exposure?

How Do We Square Surgeon General’s Warnings About Sun vs. Vitamin D’s Intake?
We will attempt to tap experts in this field to help us decipher and deal with warnings like this: “We all need to take an active role to prevent skin cancer by protecting our skin outdoors and avoiding intentional sun exposure and indoor tanning,” said Acting Surgeon General Boris D. Lushniak, MD, MPH.
What is behind the fear of the sun. We cannot say the fear is unfounded, but let’s delve into what the sun is about and the source of the fear. The sun emits solar ultra violet rays. There are three main ultraviolet rays. We know that Ultraviolet A (“UVA”) rays age skin cells and can damage DNA. These are the rays linked to long term skin damages like wrinkles and play a role in some skin cancers. Ultraviolet B (“UVB”) rays have more energy than UVA and are mostly responsible for skin cancers. On the other hand, bodies manufacture vitamin D when the UVB rays interact with 7-dehydrocholesterol (“7-DHC”) present in the skin. Ultraviolet C (“UVC”) rays have more energy than UVA and UVB, but do not penetrate the atmosphere and thus are not in the sunlight. This is a simplistic explanation, but it is a starting point to the rest of our discussion here.
A September – October 2009 Publication by the National Institute of Health conducted a study of the balance between the positive and negative effects of the solar UV-exposure. They concluded that:
“What conclusions do we draw from the findings reported above, most importantly the demonstration of an association between vitamin D-deficiency and the occurrence of numerous independent diseases, including various types of cancer? The important take home message for dermatologists and other clinicians is, that health campaigns promoting strict sun protection procedures to prevent skin cancer may induce the severe health risk of vitamin D-deficiency. There is no doubt that UV-radiation is mutagenic and is the main reason for the development of non-melanoma skin cancer. Therefore, excessive sun exposure has to be avoided, particularly burning in childhood. To reach this goal, the use of sunscreens as well as the wearing of protective clothes and glasses is absolutely important.” [emphasis added]
There seems to have been a shift in the surgeons general call for action. The focus of the 2014 Surgeon General’s Call To Action to prevent skin cancer appears to be on reducing prolonged exposure to harmful UV rays. That Call To Action states: “UV exposure is also the most preventable cause of skin cancer. This Call to Action focuses on reducing UV exposure, with an emphasis on addressing excessive, avoidable, or unnecessary UV exposures (such as prolonged sun exposure without adequate sun protection) and intentional exposure for the purpose of skin tanning (whether indoors using an artificial UV device or outdoors while sunbathing).”
This change is quite welcome. In other words, by all means use proper broad spectrum sunscreen in your everyday life, preferably in something that you use every day and wear protective covering and clothing when out in the sun, especially for a long time, but, you can’t turn vampire and avoid the sun altogether because the consequences of vitamin D deficiency are rather dire. To this end, individuals and their families must find products for both the skin and hair with natural broad spectrum sunscreen and heat protection for daily use. Then find a good safe sunscreen for when you intend to stay out in the sun, like, a visit to the beach or pool.

Differences in vitamin D deficiency incidences around the world
According to the Harvard Health Publishing study captioned “Time For more vitamin D” dated September 2008, missing out on the “sunshine vitamin” has consequences for more than just bone health. Below is a map of the United States, according to the study, depicting vitamin D absorption. The study states that “[E]xcept during the summer months, the skin makes little if any vitamin D from the sun at latitudes above 37 degrees north (in the United States, the shaded region in the map) or below 37 degrees south of the equator. People who live in these areas are at relatively greater risk for vitamin D deficiency.”
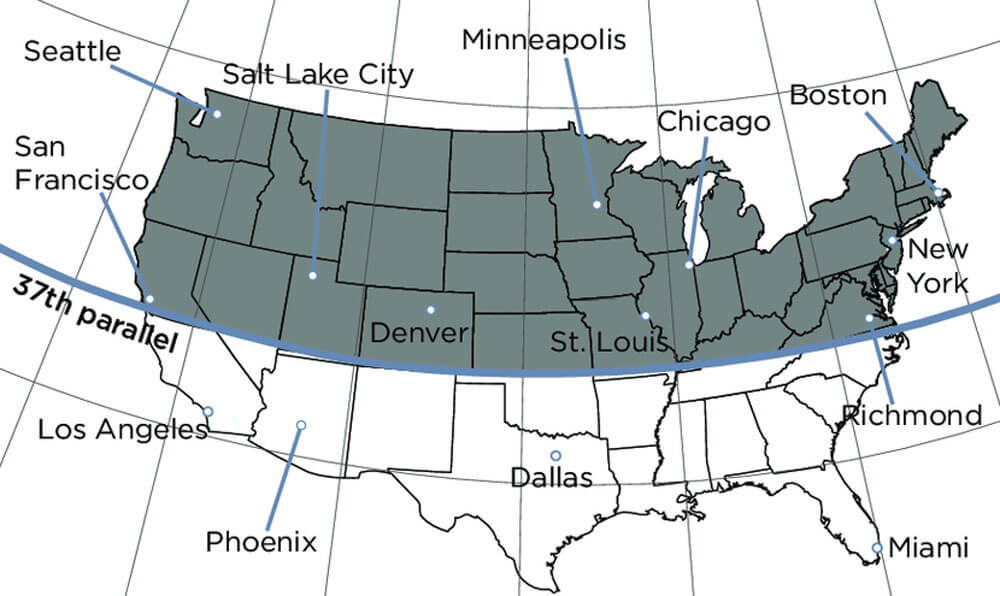
In trying to figure out how to reach 1,000 IU of vitamin D daily, that study concluded that unless you live in the South and spend a great deal of time outdoors or eat a lot of fatty fish and vitamin D-fortified foods, that vitamin D supplements are the best way to get the daily 800 to 1,000 IU per day. There are different recommendations as to required daily vitamin D intake. Speak with your medical professional for the levels that work best for you. Also, it is important to note that most people can take vitamin D supplements without any problems, but there are those with underlying medical conditions that must consult with their medical professionals before starting a vitamin D regimen to make sure that nothing is contra-indicated.
Using newly available data on worldwide cancer incidence to map cancer rates in relation to proximity to the equator, researchers at the Moores Cancer Center at University of California, San Diego (UCSD) have shown a clear association between deficiency in exposure to sunlight, specifically ultraviolet B (UVB), and kidney cancer. In an exhaustive paper captioned: “Mapping Vitamin D Deficiency, Breast Cancer, and Colorectal Cancer”, Sharif B. Mohr, Cedric F. Garland, Edward D. Gorham, William B. Grant, Robyn M. Highfill and Frank C. Garland gave us amongst others, the maps of colorectal and breast cancer by country (Figures 3-5) showing the highest incidence rates of colorectal and breast cancer in areas of low total solar irradiance and UVB. They concluded as follows:
“This is the first report to our knowledge of an adverse association between persistent cloud cover and incidence of any disease. Consistent with the association with cloud cover, places that had the lowest solar irradiance had incidence rates of breast and colorectal cancer that were several times greater than those with the highest. Countries with intermediate irradiance had intermediate incidence rates. Countries with high levels of anthropogenic sulfate aerosols (acid haze) also had significantly higher incidence rates of breast and colon cancer than those with lower levels, consistent with previous research (5). Such aerosols are the cause of acid precipitation. Their geographic distribution is nearly identical to that of acid rain (5, 20).”
“These findings support previous research indicating that solar irradiance, UVB, and photosynthesized vitamin D are associated with lower incidence of cancers of the colon (1-4, 6-15) and breast (5, 14-20).”
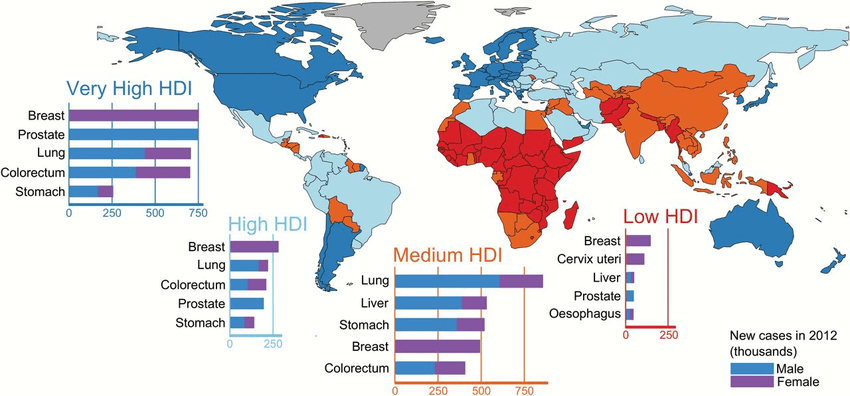
The map below uploaded by Bernard W. Stewart gives us the world map of the five most common cancers in 2012 according to levels of the Human Development Index (HDI) across the 184 countries included in GLOBOCAN.
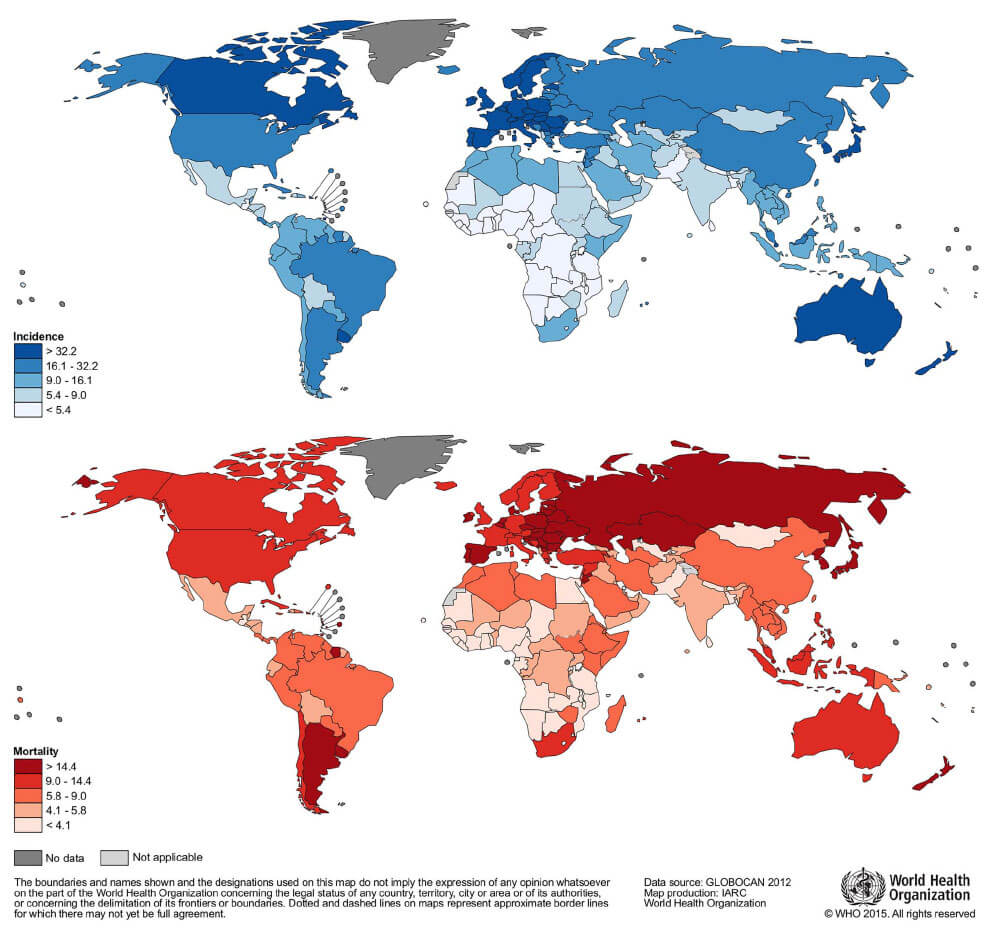
These two maps based on data, courtesy of GLOBOCAN 2012 show worldwide colorectal cancer incidence and mortality rates (age adjusted according to the world standard population, per 100,000) in males in 2012. The study published in January 2016 aimed “to describe the recent CRC incidence and mortality patterns and trends linking the findings to the prospects of reducing the burden through cancer prevention and care.”
The Future is Sunny
We hope that with the help of some eminent scholars all over the world, we have convinced you that vitamin D plays a pivotal role in our overall health and the in reduction and prevention of certain deadly diseases. If we have not convinced you, perhaps, we have opened channels to a very important dialogue to explore, discuss and understand the magnificent, vital, indispensable and positive impacts that vitamin D makes in our daily lives and why we must take steps to incorporate vitamin D in our daily lives. If we can eradicate certain diseases or seriously cut their mortality rates with simple adjustments in daily lives, why on earth wouldn’t we?
Go forth and smile into the sun. Be sure to take care of your skin and hair with products that are crafted with effective broad-spectrum sun and heat protections sourced from ingredients from nature.




Pingback: Fountain of Youth? No, But You Can Sloooooow Down Aging | The Founder's Corner | Shinkafa Hair & Body